Scientists conducted hybridisation experiments mainly on Drosophila (Fruit fly) and Guinea pig. Morgan and Castle mainly did genetic experiments on Drosophila. Because a pair of fruit flies will produce many generations with in small time.
The principles of dominance and segregation are explained by monohybrid cross.
1. Monohybrid cross - definition
A cross made to study the inheritance of one character or two . contrasting forms or two different alleles is known as monohybrid cross.
Animal example:
Crossing of black and white Guinea pigs is the monohybrid cross. In this cross, the inheritance of colour character or black and white contrasting forms or ‘B’ and ‘b’ alleles inheritance is observed.
2. Phenotypic explanation
When pure black and white Guinea pigs were crossed, all ‘F1’ individuals are black in colour. These are monohybrids. By observing ‘F1’ individuals, e can explain the principle of dominance. 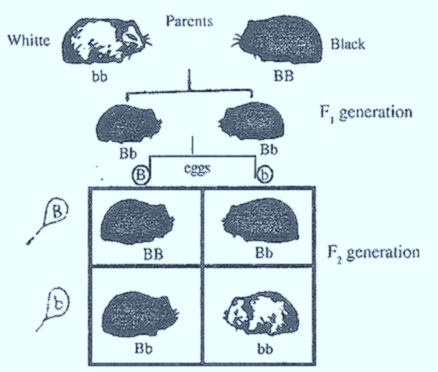
A. Principle of dominance - Definition:
The principle of dominance states that when two contrasting forms (Black, White) were crossed,’the contrasting from that appeared in ‘F1’ generation is called dominant form(Black). The contrasting form that did not appear in ‘F1’ generation is called recessive contrasting form (white). The above experiment indicates that the black contrasting form is dominant over white form in Guinea pigs
B. Crossing of ‘F1’ individuals:
When ‘F1’ Black Guinea pigs were crossed, in ‘F2’ both black and white are produced. They (Black and White) are in the ratio of 3/4 or 75%: 1/4 or 25%.